Public Opinion Analysis of Transportation Policy using Social Media Data: Case Study on the Delhi Odd-Even Policy
Pranamesh Chakraborty, Anuj Sharma
To appear in Transportation in Developing Economies
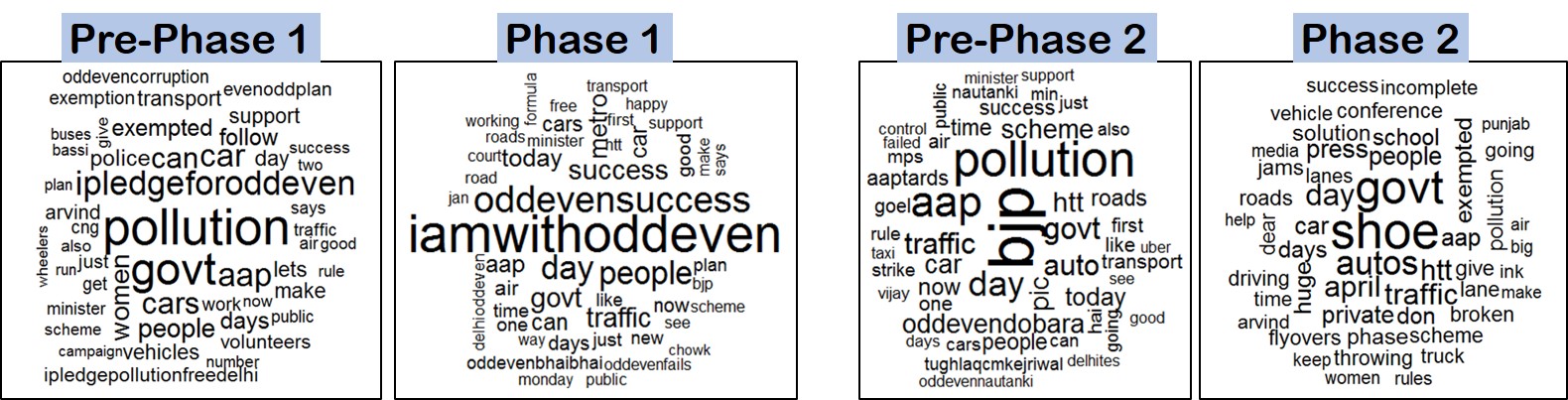
Abstract: Twitter, a microblogging service, has become a popular platform for people to express their views and opinions on different issues. Sentiment analysis of tweets can help in understanding public opinion on different government decisions. This paper used Twitter data to extract sentiments of people during the Phase 1 and Phase 2 of the odd-even policy implemented by the Delhi government to curb the air pollution and improve traffic flow. In this study, we used four different lexicon based approaches: Bing, Afinn, National Research Council (NRC) emotion lexicon, and Deep Recursive Neural Network based Natural Language Processing software (CoreNLP) to extract sentiments from tweets and thereby assess overall public opinions. The daily trend obtained for each phase was normalized with the number of tweets and then compared using Granger causality test. The causality test results showed that the trends obtained during the two phases were significantly different from each other. In particular, public sentiments were found to mostly turn negative during the later stage of the Phase 2 which indicates fading away of the public enthusiasm and positiveness towards the policy during the later stages of the policy implementation.
Citation: P. Chakraborty and A. Sharma. Public Opinion Analysis of Transportation Policy using Social Media Data: Case Study on the Delhi Odd-Even Policy, Transportation in Developing Economies (to appear).
